Cover crops have many benefits. They can improve soil quality characteristics like drainage, tilth, reduced compaction, etc. But one of the most unique functions is their ability to improve soil nutrients organically. When a cover crop with nutritional benefits is grown, the amount of fertilizer needed throughout the year is reduced. Plus, you still get to enjoy the many other benefits cover crops have to offer. Now don’t get me wrong, I’m not saying cover crops are a magical solution to all your nutrient needs. But they do contribute enough to warrant their growth. So how exactly do cover crops increase soil nutrients? By fixing nitrogen and scavenging for mineral nutrients. The most popular seeds to grow for these benefits are legumes, grains, and grasses.
What is Nitrogen Fixation?
Nitrogen fixation is the process of transferring atmospheric nitrogen into forms usable by plants in the soil. Plant roots are unable to absorb the nitrogen found in the form of N2 (atmospheric Nitrogen gas). Instead, all plants absorb nitrogen in the form of ammonia (NH3). This situation is comparable to a person's need for liquid water. You could be surrounded by all the water vapor in the world. But that won’t do you much good if you are thirsty. The organisms responsible for transforming nitrogen gas into an ammonia form that is usable are soil rhizobia bacteria that work in root nodules formed on legume plant roots. When legume cover crops are grown, they take advantage of this symbiotic relationship that results in better soil health for the next growing season.
For the greatest nutrient benefits, allow the cover crop to grow for 5-6 weeks. This will give it enough time to begin fixing nitrogen. Then allow the plant matter to break down and become incorporated back into the soil. Allow at least 2-3 weeks of rest between terminating a cover crop and planting your garden. This will allow the nitrogen that was tied up in the plant matter to be released back into the soil for use by the next crops.
Legumes for Nitrogen Fixation
How Do Cover Crops Scavenge For Nutrients?
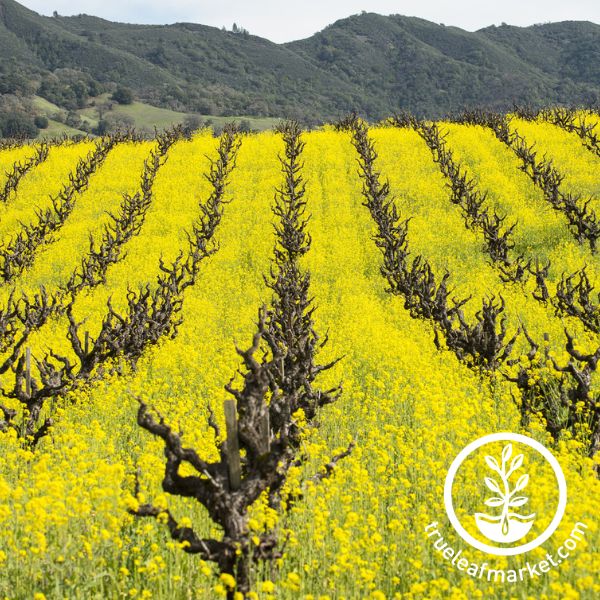
While some plants are able to transfer nitrogen into usable forms, others are able to pull leaching nutrients back into the upper root range. Throughout the growing season, water carries nutrients through the soil from the surface down. Sometimes this means valuable nutrients travel beyond the central root range. Plants like canola rapeseed, rye, mustard, and radishes are able to pull those nutrients closer to the surface for use by the next crop. This not only reduces the amount of fertilizer needed but also reduces the risk of nitrogen-contaminated groundwater.
For the best nutrient development, consider growing a cover crop mix. This will provide the most optimal soil benefits as weeds are suppressed, nitrogen is both fixed and scavenged for and generous biomass is produced. Biomass is plant matter that creates organic matter once it is broken down. Organic matter is incredibly important as it contributes to the carbon that every living thing is made of.






























0 comments
No comments yet! Be the first to start a conversation.